ZStack Cloud Platform
Single Server, Free Trial for One Year
Comprehensive Data Center Infrastructure Solutions.
4S-compliant productized private cloud and seamless hybrid cloud
Offer a user experience consistent with VMware virtualization
A robust catalog of ready-to-deploy product
Supports storage resource pools with capacities exceeding PB levels
Covering scenarios from core to edge, cloud to cloud- native, and data management to AI
Deploy ZStack for scenario from datacenter to the edge.
ZStack provides innovative cloud infrastructure for ten major industries.
Comprehensive product documentation and tools
Upholding the value of Customer First and the mission of Serving Customer, ZStack is dedicated to providing secure and stable services for customers.
To educate ZStack partners and interested individuals about cloud computing and to cultivate cloud computing talent.
ZStack provides innovative cloud infrastructure for ten major industries

The report provides three major
solutions and customer case studies for transitioning from VMware to ZStack.
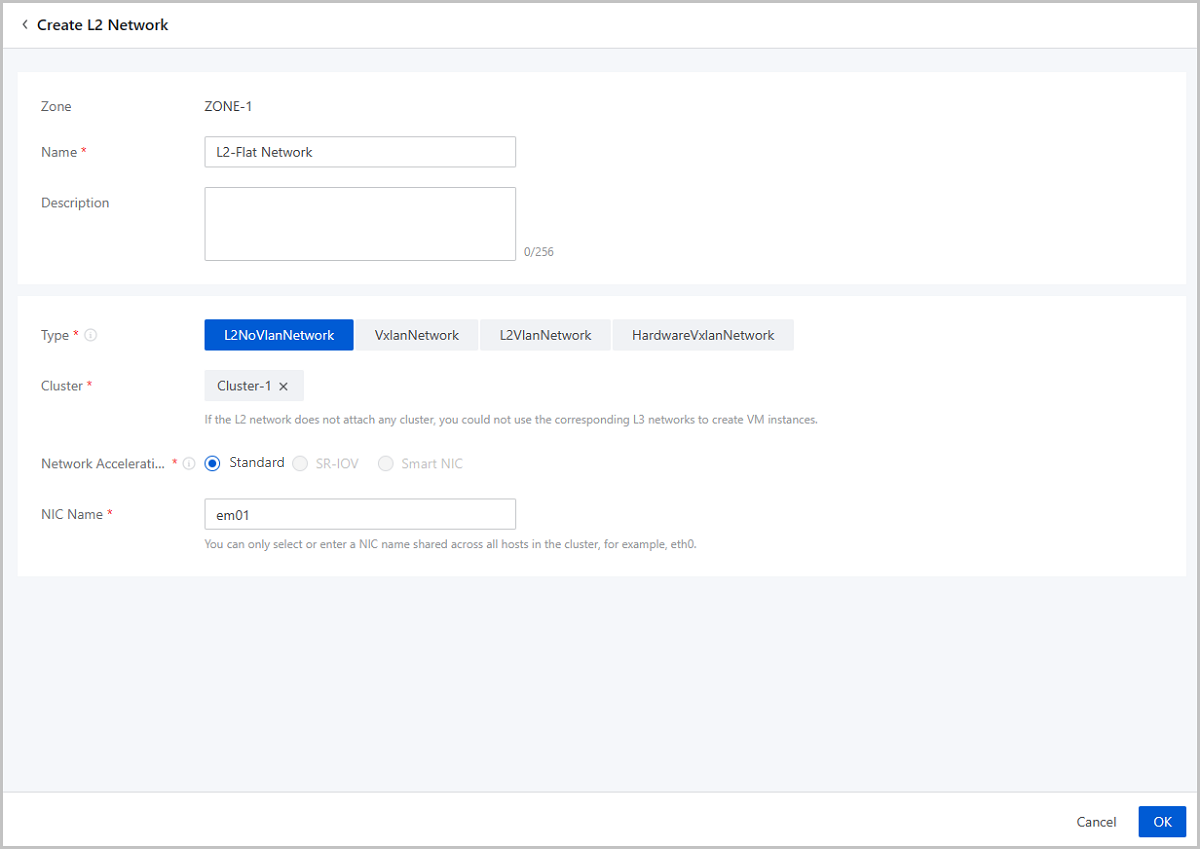
ZStack Cloud supports IPv4 flat networks, IPv6 flat networks, and public networks. This section describes basic deployments of IPv4 flat networks and IPv6 flat networks.
IPv4, known as Internet Protocol version 4 which defines IP addresses in a 32-bit format, is the most popular Internet Protocol version across the globe. ZStack Cloud flat networks support the IPv4 protocol. This topic mainly describes the basic deployment of IPv4 flat networks.
| Flat Network | Configurations |
|---|---|
| NIC | em01 |
| VLAN ID | No VLAN |
| IP Range | 172.20.108.40-172.20.108.50 |
| Netmask | 255.255.0.0 |
| Gateway | 172.20.0.1 |
| DHCP IP | 172.20.180.41 |
 Note:
Note:  Note:
Note: 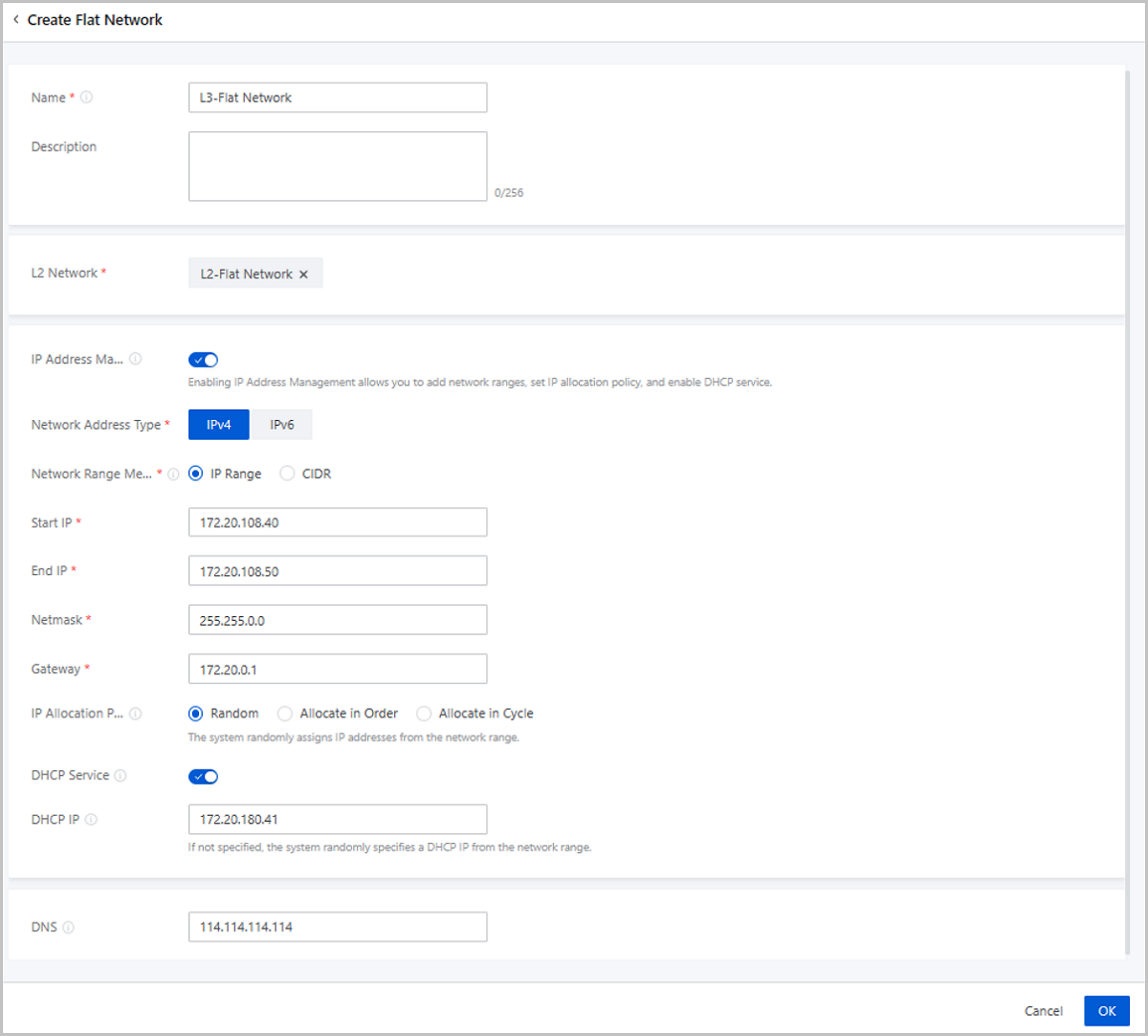
On the main menu of ZStack Cloud, choose Resource Center > Resource Pool > Virtual Resource > VM Instance. On the VM Instance page, click Create VM Instance. Then, the Create VM Instance page is displayed. On the displayed page, create two VM instances by using the IPv4 flat network, for example, VM-1 and VM-2.
Expected result: The two VM instances (VM-1 and VM-2) on the same network range can communicate with each other.
ping VM-2.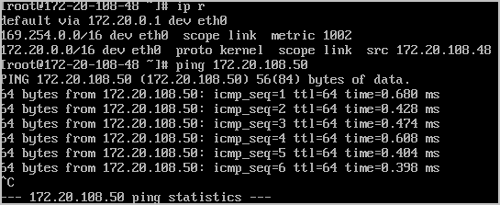
ping VM-1.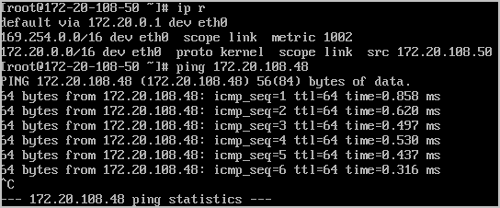
So far, we have introduced the basic deployments of the IPv4 flat network.
IPv6 is Internet Protocol version 6 that defines IP addresses in a 128-bit format. IPv6 resolves the long-anticipated problem of IPv4 address exhaustion, so many devices can be connected to the Internet. ZStack Cloud flat networks support the IPv6 protocol. This topic describes the basic deployment of IPv6 flat networks.
| Flat Network | Configurations |
|---|---|
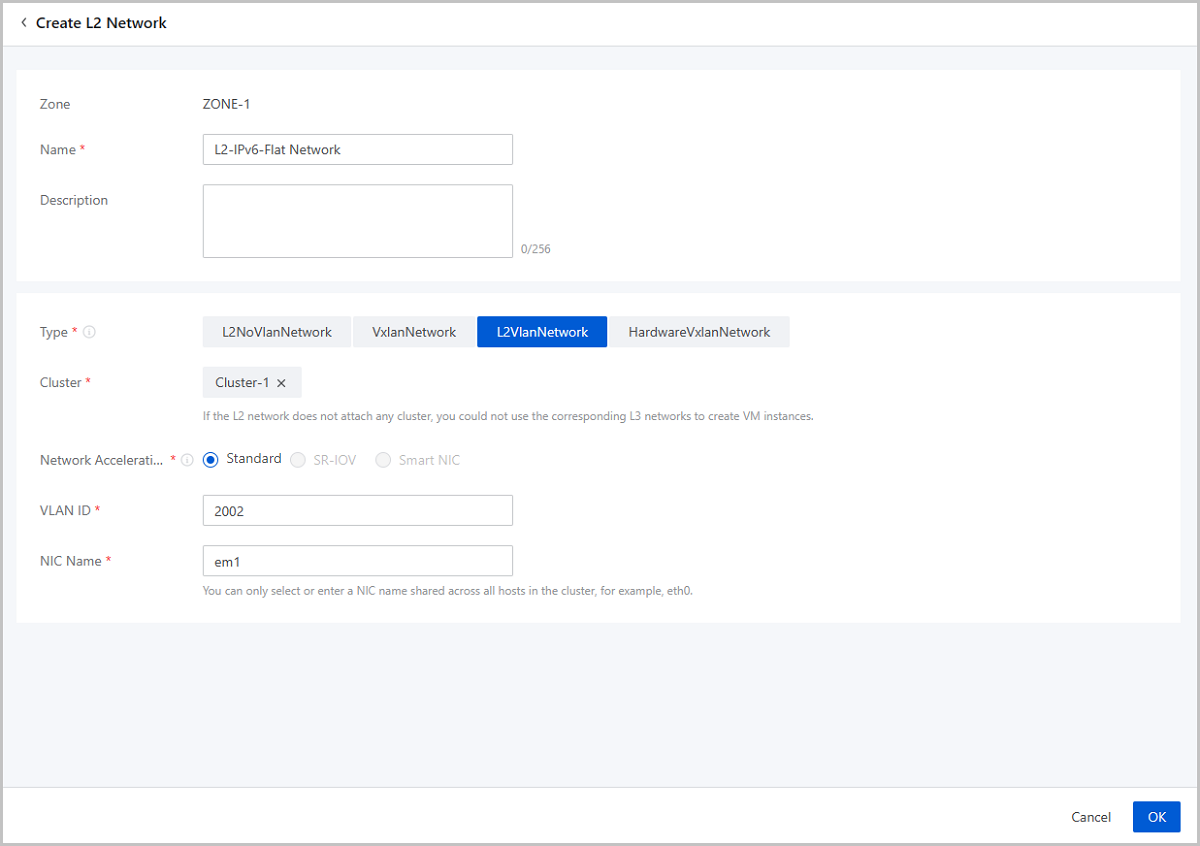
| NIC | em1 |
| VLAN ID | 2002 |
| IP Range | 234e:0:4567::2-234e:0:4567:0:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff |
| Prefix length | 64 |
| Gateway | 234e:0:4567::1 |
| DHCP IP | 234e:0:4567::3 |
| DNS | 240c::6644 |
 Note:
Note:  Note:
Note: 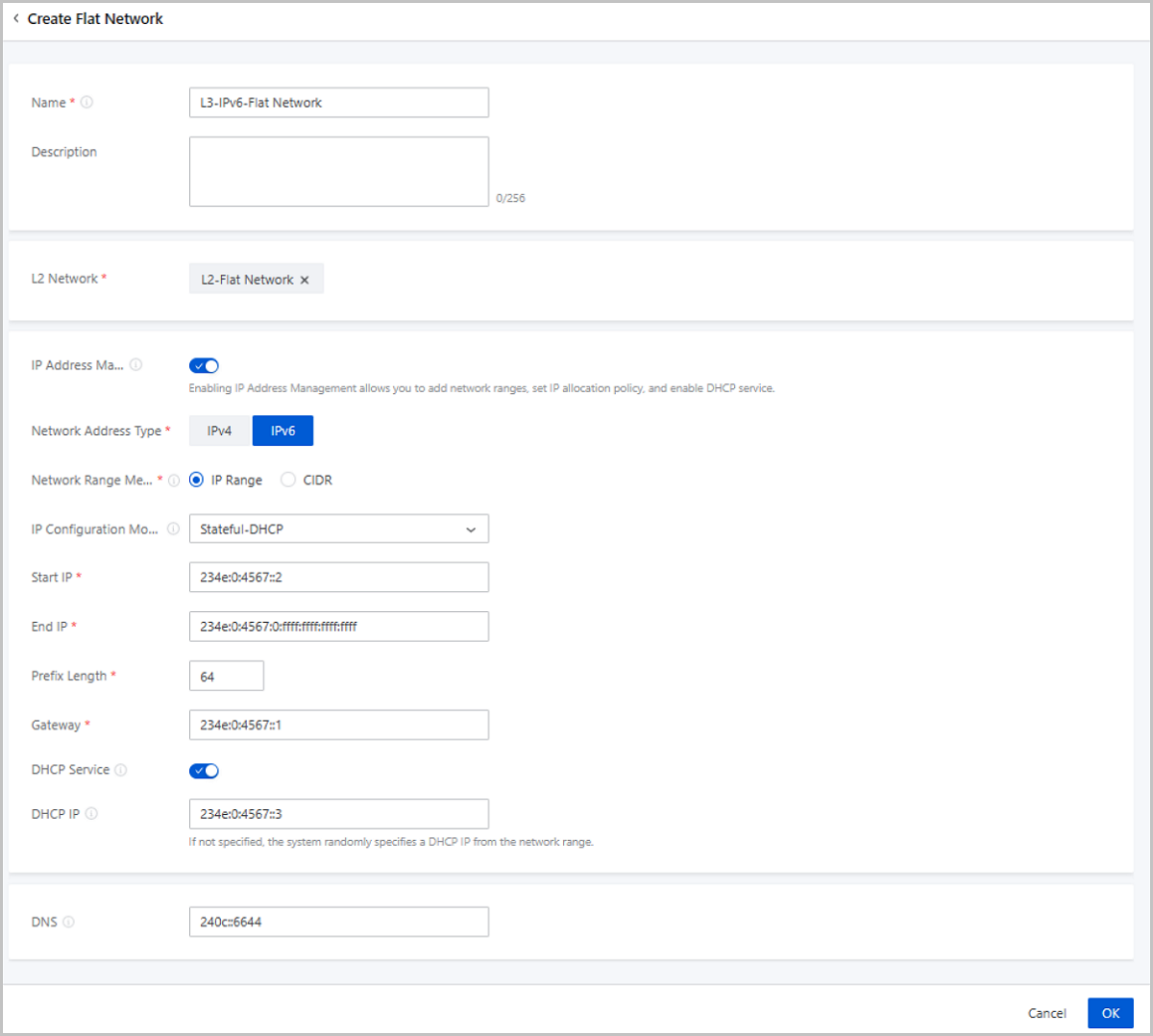
On the main menu of ZStack Cloud, choose Resource Center > Resource Pool > Virtual Resource > VM Instance. On the VM Instance page, click Create VM Instance. Then, the Create VM Instance page is displayed. On the displayed page, create two VM instances by using the IPv6 flat network, for example, VM-1 and VM-2.
[root@loaclhost~]# dhclient -6 eth0 //eth0 indicates the NIC name. Note: The address that begins with FE80 is the link-local address instead of the expected address.
Note: The address that begins with FE80 is the link-local address instead of the expected address.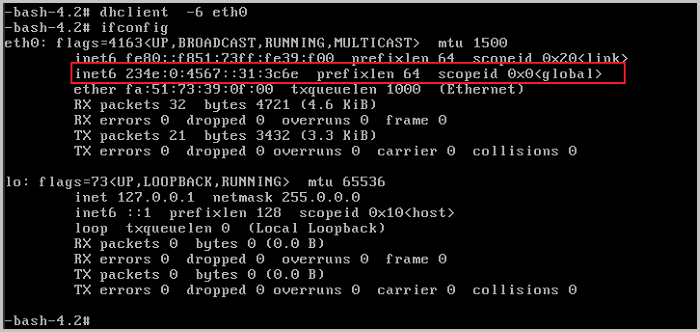
Expected result: The two VM instances (VM-1 and VM-2) on the same network range can communicate with each other.
ping VM-2.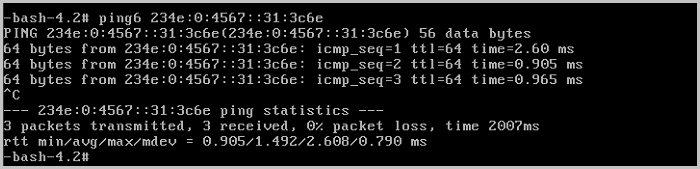
ping VM-1.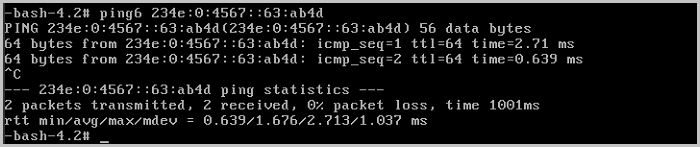
So far, we have introduced the basic deployments of the IPv6 flat network.
IP Address Management (IPAM) is a service for the allocation and management of IP addresses on an L3 network. Enabling IPAM for an L3 network requires you to add network ranges from which IP addresses are allocated to the resources on this L3 network automatically. ZStack Cloud allows you to disable IPAM when creating a flat network which does not need network ranges and other relevant parameters. You can allocate and manage IP addresses of resources on this flat network by yourself without the restriction of network ranges. This topic describes the deployment of a flat network disabled with IPAM.
| Flat Network | Configurations |
|---|---|
| NIC | eth0 |
| VLAN ID | 2002 |
| Flat Network | Configurations |
|---|---|
| IP address | 172.20.60.107 |
| Netmask | 255.255.0.0 |
| Gateway | 172.20.0.1 |
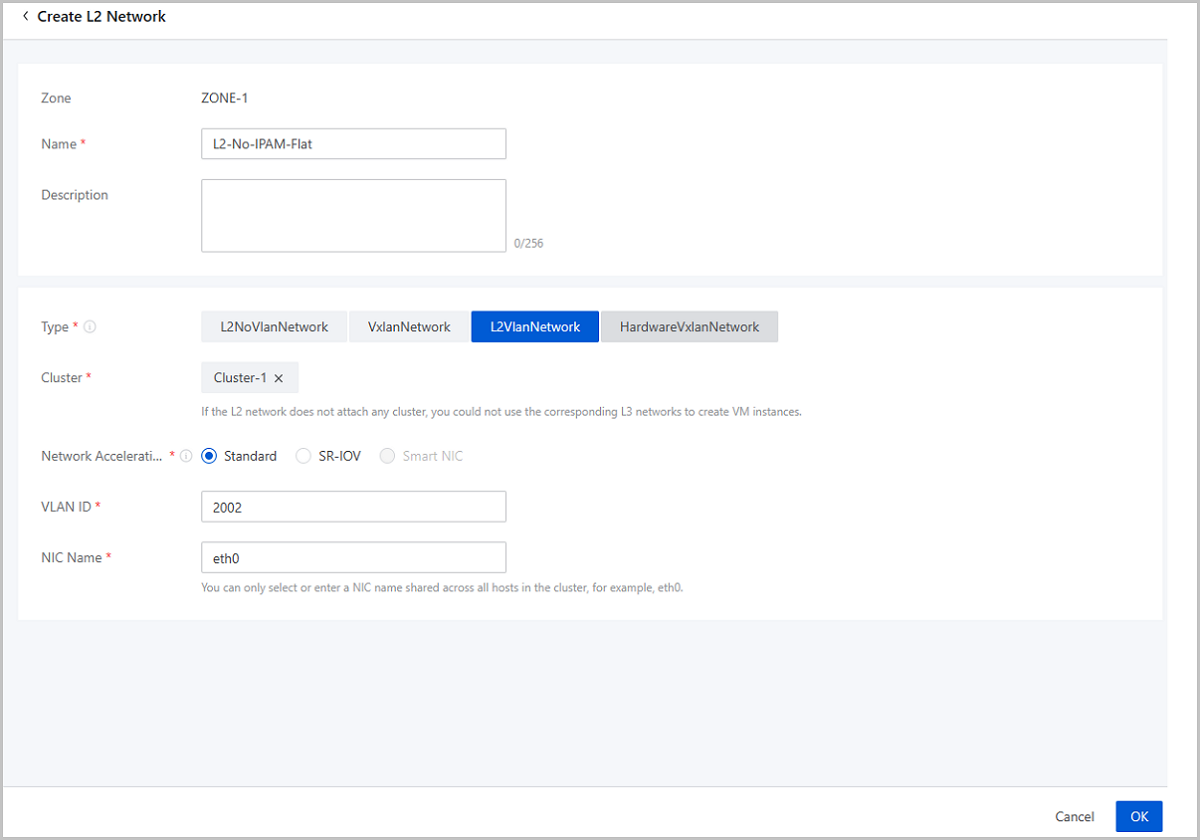
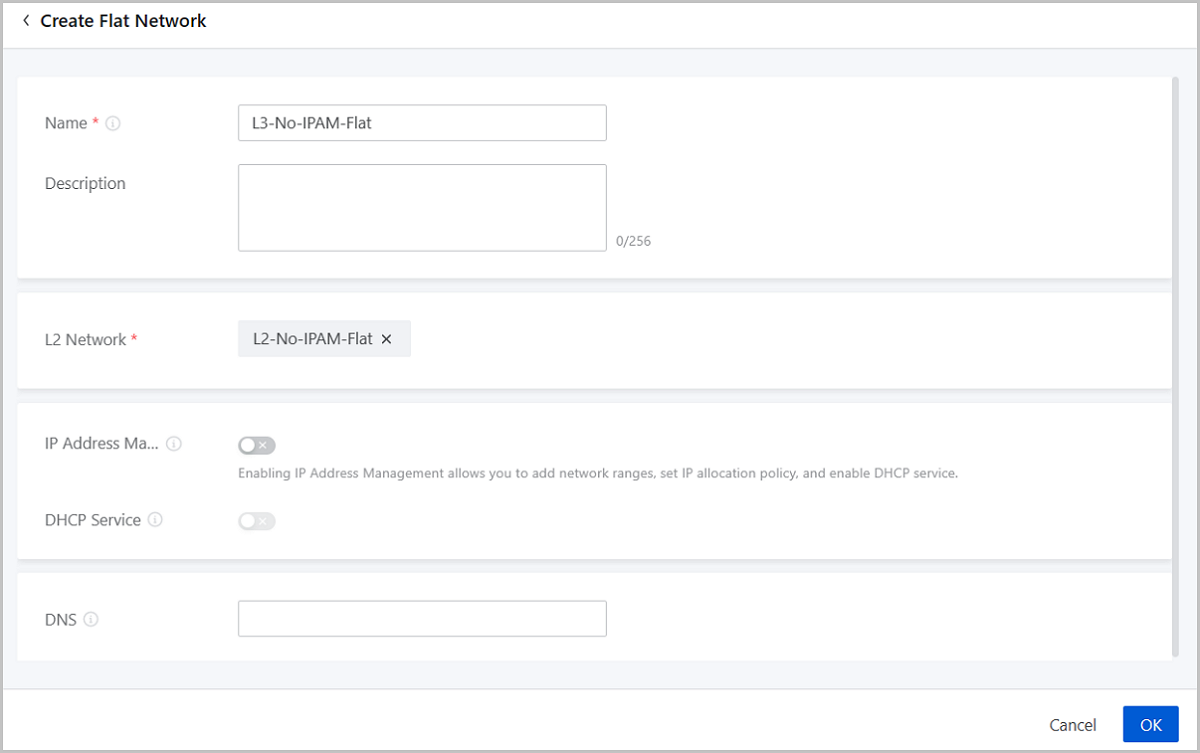
 Note: If you configure an IP address in the VM instance, the IP address cannot be read or managed by the Cloud currently.
Note: If you configure an IP address in the VM instance, the IP address cannot be read or managed by the Cloud currently. Note:
Note: 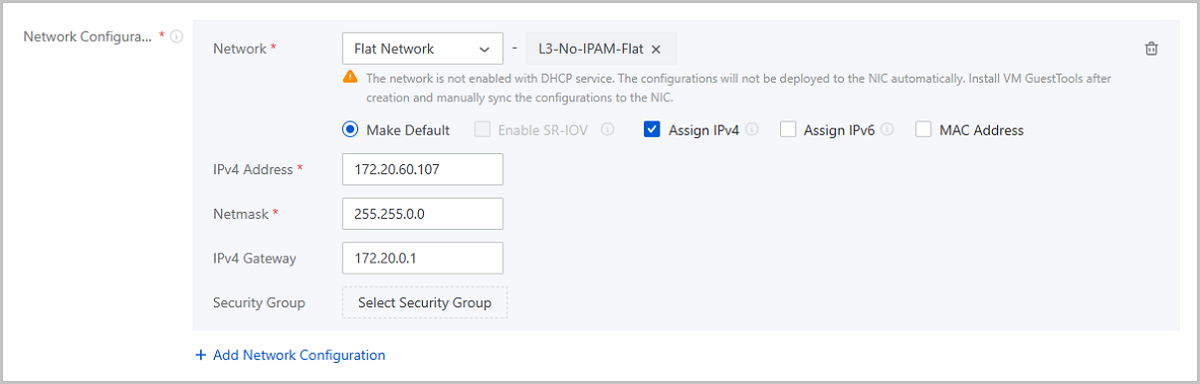
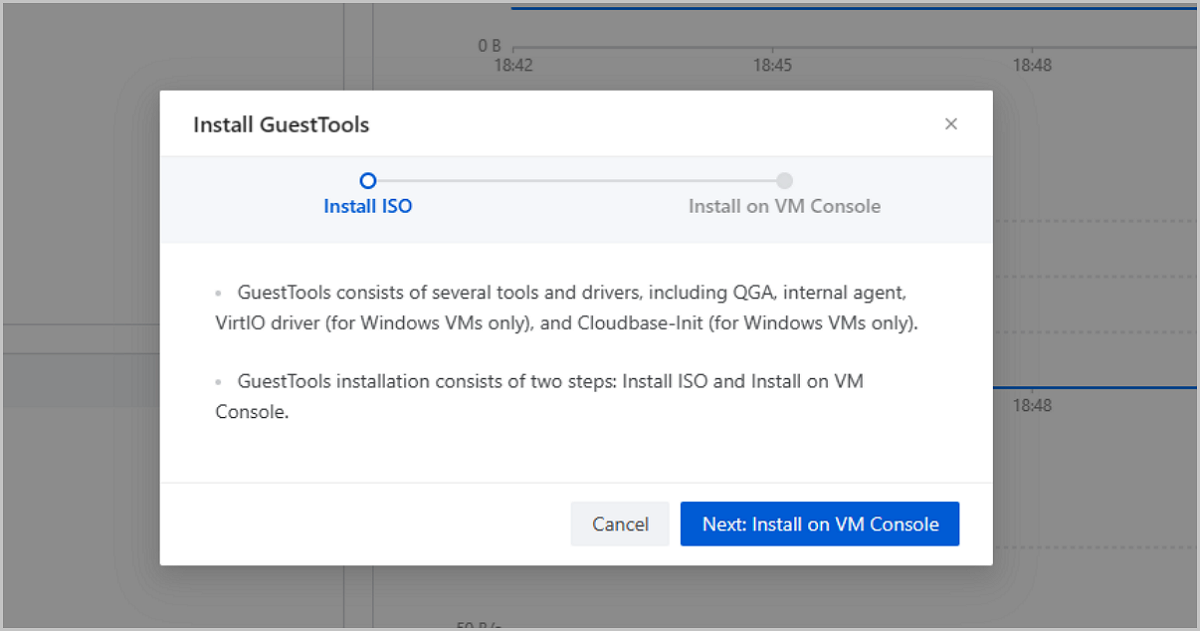
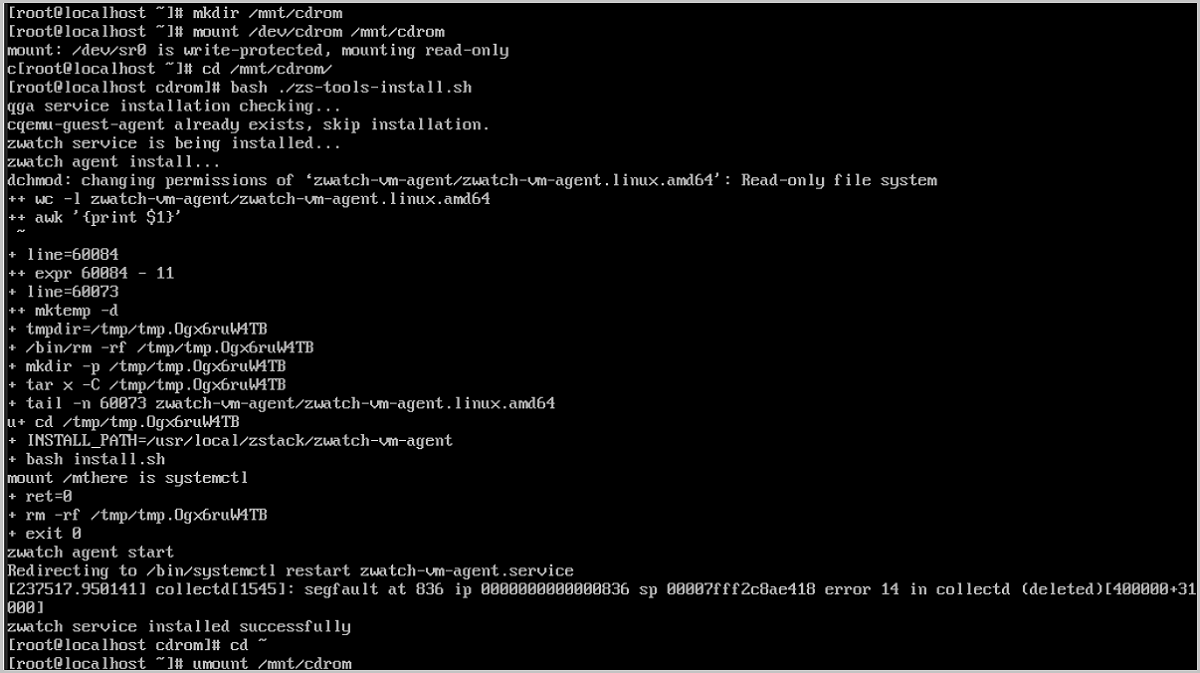
# Create a mount point. mkdir /mnt/cdrom # Attach the CD-ROM image. mount /dev/cdrom /mnt/cdrom # Install GuestTools. cd /mnt/cdrom/ bash ./zs-tools-install.sh # Unmount the CD-ROM image (optional). cd ~ umount /mnt/cdrom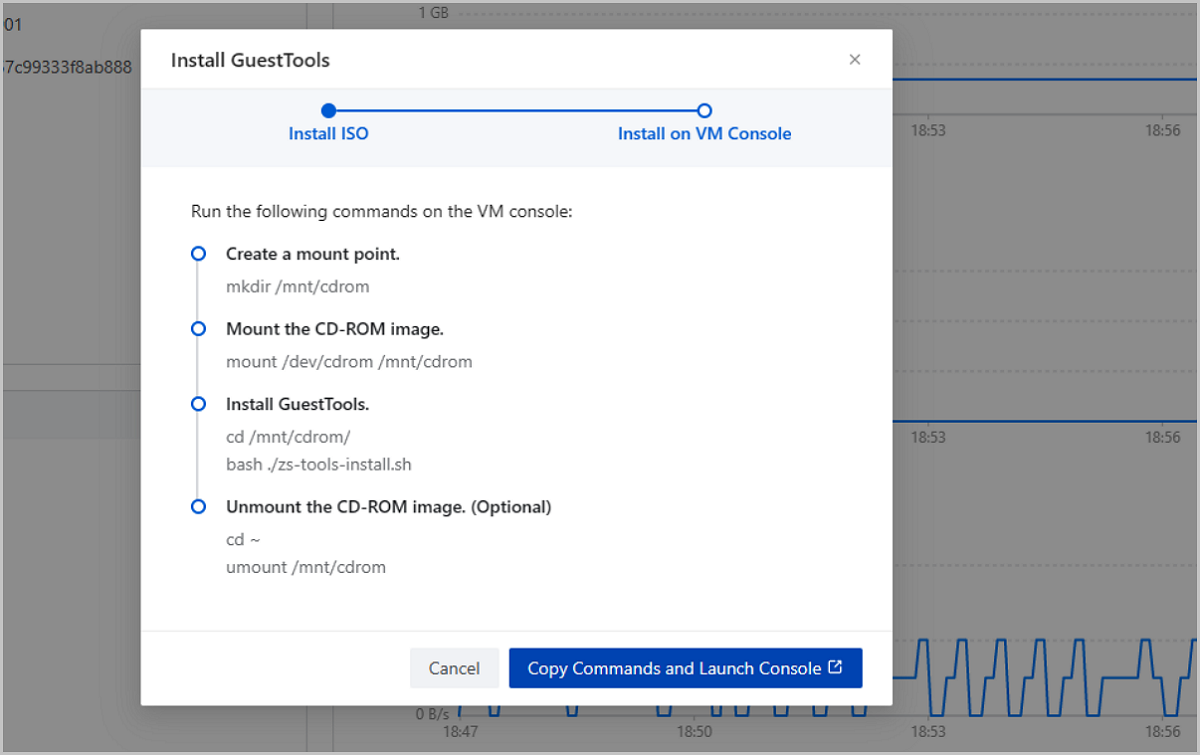
 Note: If you configure an IP address in the VM instance, you can skip this step.
Note: If you configure an IP address in the VM instance, you can skip this step. Note: If you configure an IP address in the VM instance, you can skip this step.
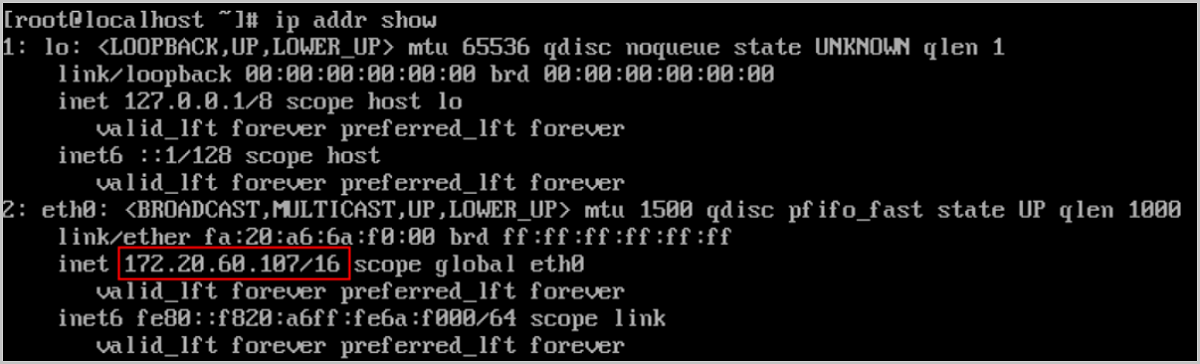
Note: If you configure an IP address in the VM instance, you can skip this step.Expected result: The IP address assigned on the Cloud can be queried in the VM instance.
Log in to the VM-Self-Managed-IP and check the VM IP address.
 Note: If you configure the IP address in the VM instance, you can skip this validation.
Note: If you configure the IP address in the VM instance, you can skip this validation.Download Document Archives

