- Account Home
- Language
- News
- Products
-
Cases
By Service
- Help & Support
- Partners & Training
- About Us
Backup Service, which is business-centered, integrates the scheduled incremental backup, scheduled full backup, and other backup technologies to ZStack Private Cloud. With Backup Service, multiple backup solutions are supported, such as local backup, remote backup, and Public Cloud backup solutions. Select an appropriate backup solution according to your own business needs.
Backup Service is a separate feature module. To use this service, purchase both the Base License and the Plus License of BareMetal Management. The Plus License cannot be used independently.
Backup Service can be applied to the following three typical scenarios: local backup, remote backup, and Public Cloud backup.
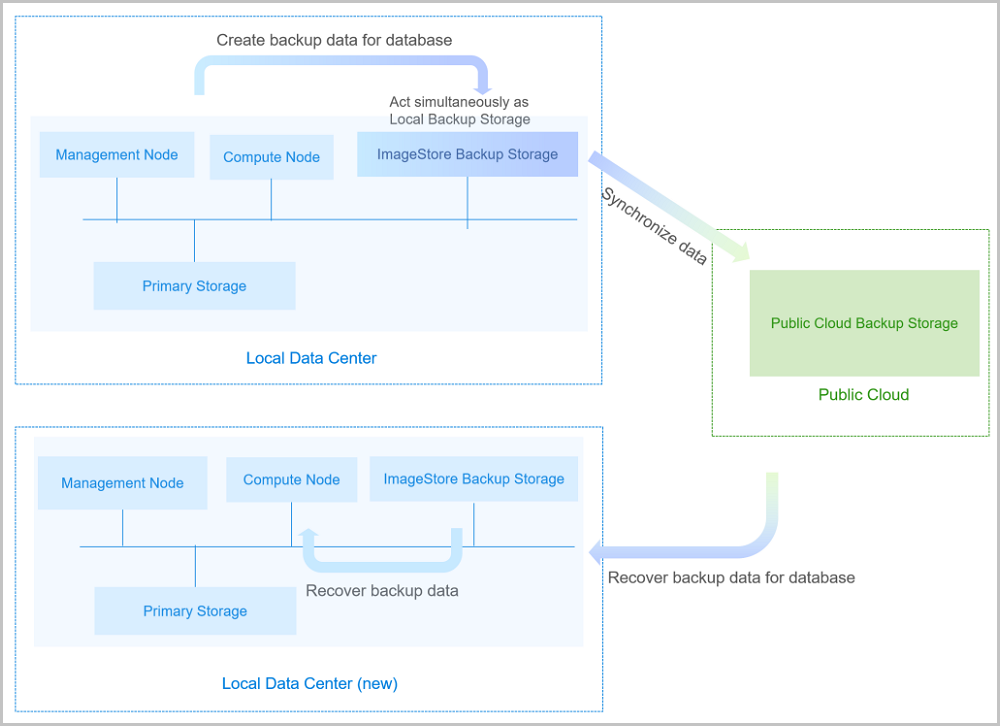
A local ImageStore backup storage can act as the Local Backup Storage to store scheduled backup data of the local VM instances, volumes, and management node databases. Meanwhile, the seamless switchover between the master local backup storage and the standby local backup storage is supported, which effectively ensures your business continuity.
If your local data is mistakenly deleted, or data in the local primary storage is damaged, you can recover the backup data from the local backup storage, as shown in Local Backup Scenario-1
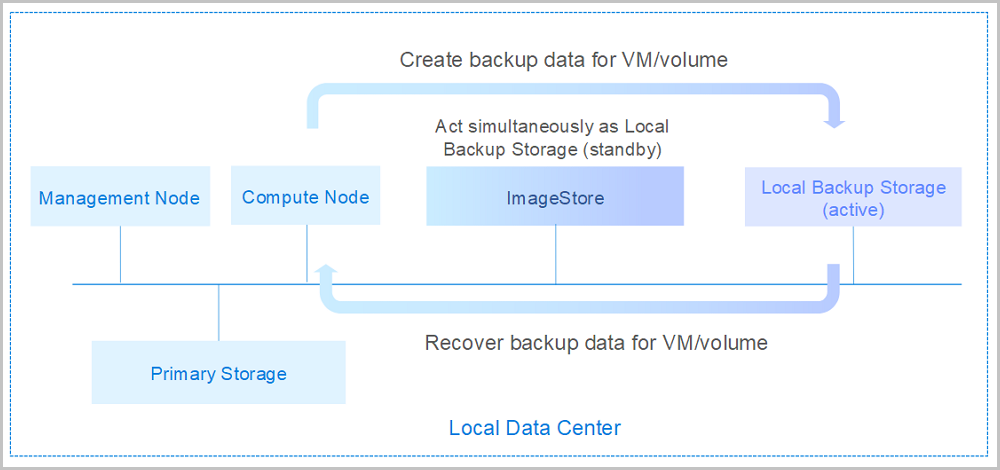
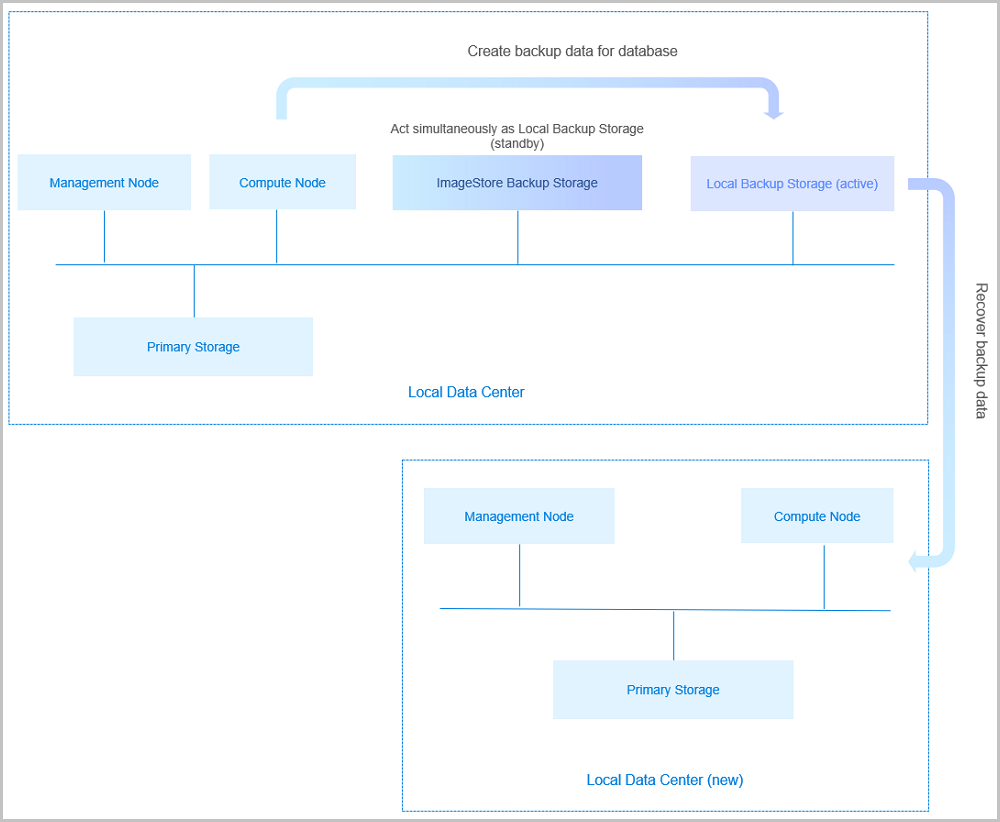
If you encounter a disaster in your local data center, you can rely totally on your local backup storage to rebuild your data center and recover your business, as shown in Local Backup Scenario-2.
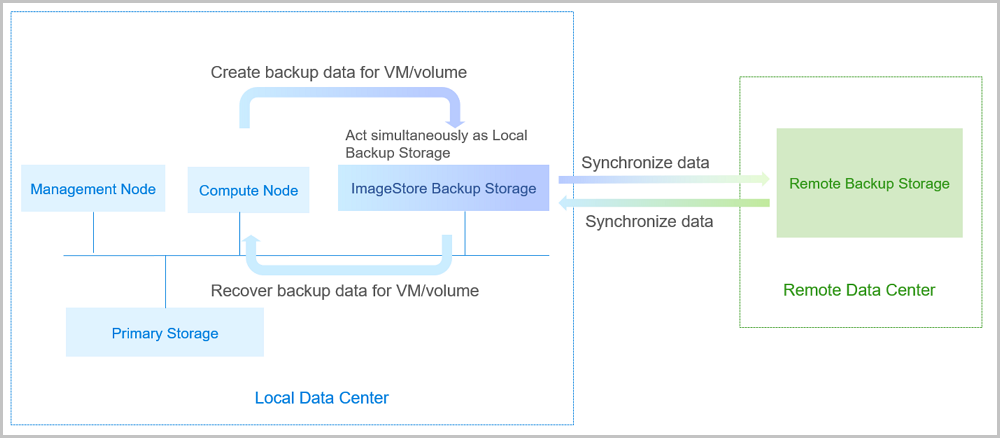
A storage server in a remote data center can act as the Remote Backup Storage to store the scheduled backup data of the local VM instances, volumes, and databases. The backup data needs to be synchronized to the remote backup storage from the local backup storage.
If your local data is mistakenly deleted, or data in the local primary storage is damaged, you can recover the backup data from the remote backup storage, as shown in Remote Backup Scenario-1
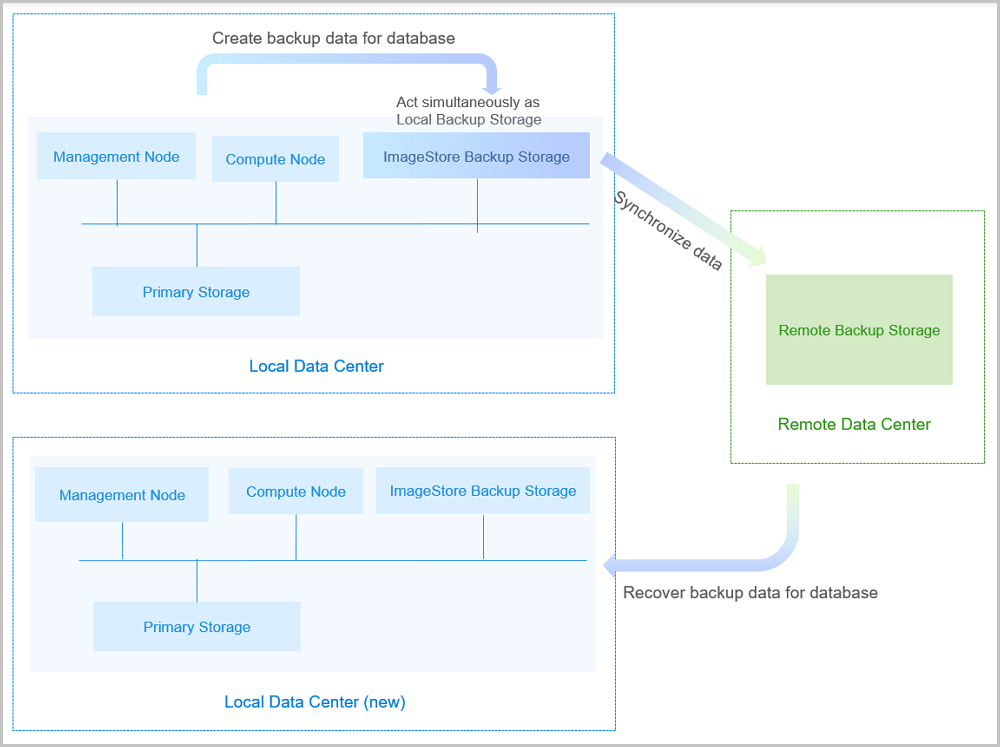
If you encounter a disaster in your data center, you can rely totally on your remote backup storage to rebuild your data center and recover your business, as shown in Remote Backup Scenario-2.
The storage server in the Public Cloud can act as the Public Cloud Backup Storage to store the scheduled backup data of the local VM instances, volumes, and databases. The backup data can be synchronized to the Public Cloud backup storage from the local backup storage.
If your local data is mistakenly deleted, or data in the local primary storage is damaged, you can recover the backup data from the Public Cloud backup storage, as shown in Public Cloud Backup Scenario-1.
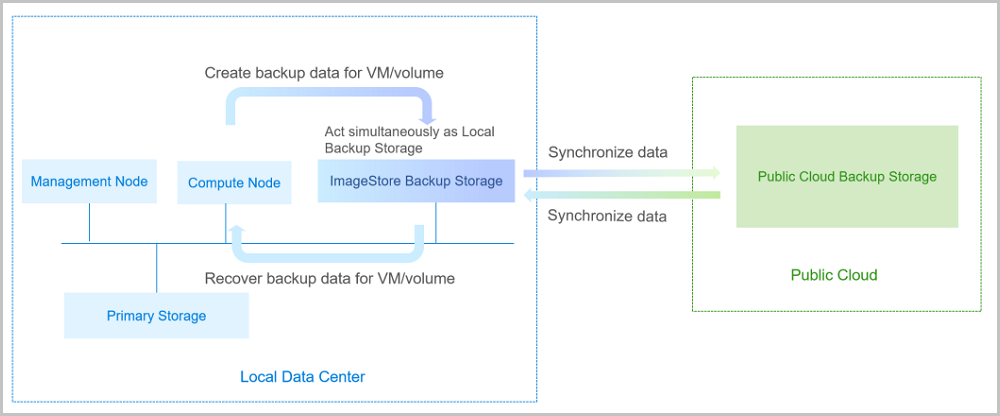
If you encounter a disaster in your data center, you can rely totally on your Public Cloud backup storage to rebuild your data center and recover your business, as shown in Public Cloud Backup Scenario-2.
A backup task enables you to back up local VM instances, local volumes, or local MN database (database) on schedule to a specified local backup storage, and also to synchronize backup data to a specified remote backup storage (offsite backup storage or Public Cloud backup storage.
The backup task overview page displays backup task executions of VM instances, volumes, and database, where backup tasks within a time range are calculated and analyzed in visual graph. As a result, you can directly get a whole picture of all backup tasks.
incrementalBackup.maxNum to set the default value to 64 globally, an indication that after 63 times of backup tasks are performed, a full backup will be performed once.[root@localhost ~]# zstack-cli #Run CLI. admin>>> LogInByAccount accountName=admin password=password #Log in to CLI. Default user name/password: admin/password. admin >>>UpdateGlobalConfig category=volumeBackup name=incrementalBackup.maxNum value=10 #Modify the maximum incremental backups. { "inventory": { "category": "volumeBackup", "defaultValue": "64", "description": "the maximum numbers of continuous incremental backup", "name": "incrementalBackup.maxNum", "value": "10" }, "success": true } Note:
Note: For example, assume that you expunge the local backup data of a VM instance or volume, and expunge this VM instance or volume restored from this backup data. At this time, performing the clear data button will release the storage space for this local backup storage.
Back to Top
Email Us
contact@zstack.ioEmail Us
contact@zstack.ioEmail Us
contact@zstack.ioThe download link is sent to your email address.
If you don't see it, check your spam folder, subscription folder, or AD folder. After receiving the email, click the URL to download the documentation.Thank you for using ZStack products and services.
Submit successfully.
We'll connect soon.Thank you for using ZStack products and services.