- Account Home
- Language
- News
- Products
-
Cases
By Service
- Help & Support
- Partners & Training
- About Us
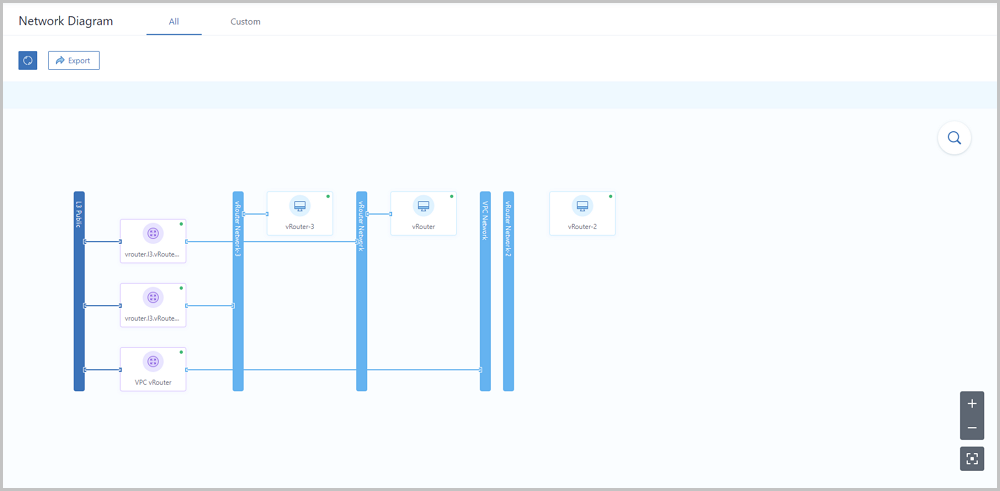
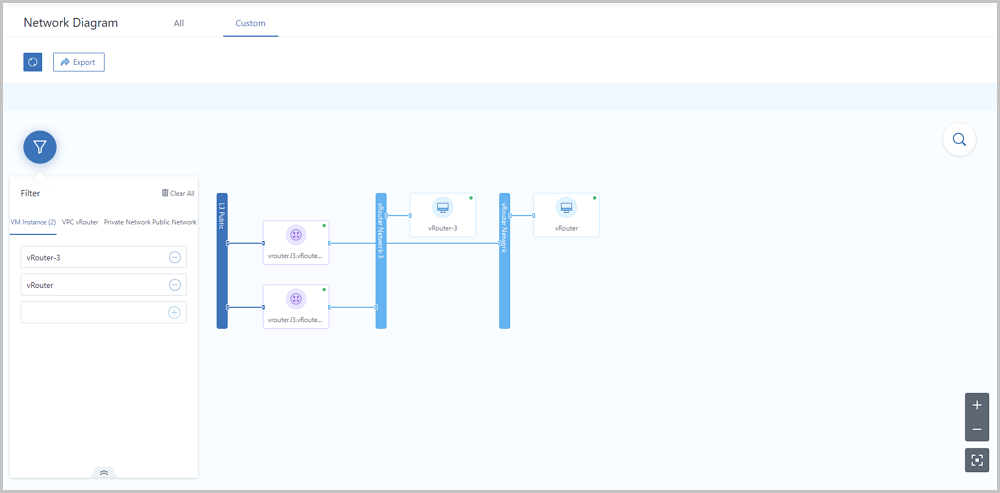
The diagram not only provides a direct display of global diagrams on the cloud and helps you to analyze network problems, but also enables you to generate custom network diagrams where you can quickly locate the resource states.
By adding SDN controllers, you can take over the SDN networks of hardware switches on the cloud to lower the network latency and improve the VXLAN network performance.
An L3 network can serve as a sub-resource of the L2 network. Mainly based on the L2 network, the L3 network provides the network configurations for VM instances, including the IP range, gateway, DNS and network service.
ZStack provides the network services of VM instances by using custom Linux VM instances to serve as routing devices. Related route resources mainly include vRouters, vRouter images, vRouter offerings, and vRouter tables.
VPC is the custom private cloud network environment that is jointly comprised by a VPC vRouter and a VPC network. VPC can help enterprise users to build a logically isolated private cloud. In addition, VPC features lie at the flexible network configuration, secure, reliable isolation, and optimization of east-west network traffic direction. A VPC network can act as a private VPC network to provide multiple network services by using a VPC vRouter.
You need to first create an L2 network, and then use it to create an L3 network. Finally, use these networks to provide multiple network services.
For more information about the network service, see Network Service.
ZStack public network, flat network, and VPC network support two network protocols: IPv4 and IPv6. You can create an IPv4 network, an IPv6 network, or an IPv4+IPv6 network as needed.
ZStack supports the network diagram feature. Notice that the Cloud not only supports the global diagram (All), but also allows you to generate your own diagram (Custom) by selecting resources where you can quickly locate the resource states.
| Router/VM State | Dot Color |
|---|---|
| Starting | Blue |
| Running | Green |
| Stopping | Blue |
| Stopped | Red |
| Rebooting | Blue |
| Deleting | Blue |
| Deleted | Grey |
| Migrating | Blue |
| Expunging | Blue |
| Pausing | Blue |
| Paused | Grey |
| Recovering | Blue |
| Unknown | Yellow |
Back to Top
Email Us
contact@zstack.ioEmail Us
contact@zstack.ioEmail Us
contact@zstack.ioThe download link is sent to your email address.
If you don't see it, check your spam folder, subscription folder, or AD folder. After receiving the email, click the URL to download the documentation.Thank you for using ZStack products and services.
Submit successfully.
We'll connect soon.Thank you for using ZStack products and services.